At the end of the procedure it may be decided that a small tube (a single J or double J stent) is left inside your ureter.
What is a double J (or JJ)?
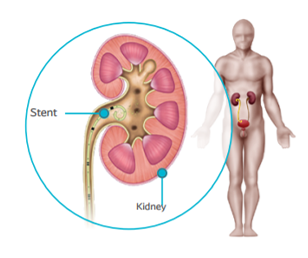
A JJ stent is a small tube placed inside your urinary tract without incision (natural way) or during an open surgery. The surgeon will check if it is well in place thanks to a radiology system after the procedure. Inserted into the ureter, the stent goes from the kidney to the bladder. Both tips of the stent are curved, hence its name of double J or JJ. It doesn’t stick out from the body, it is internal and so invisible. In some cases, a the removal thread may remain visible out of your urethra, which will help the surgeon to remove the stent after a few days.
JJ ureteral stents are composed from a variety of different materials with various rigidities to meet the needs of the physician and the patient. As a foreign body in your ureter, the stent may be associated with some discomfort. Some firm materials can generate more discomfort to the patients. Hydro-coated silicone stents have demonstrated their capacities to reduce urinary symptoms, patient discomfort, and mineral deposit along the stent (encrustation).1,2
Discover our silicone double loop ureteral stents
Short, medium and long-term stents (from few days to several months) of different lengths and diameters are available.3,4
The purpose of the stent is to help the urine flow towards the bladder and prevent any renal colic. Therefore, the JJ stent dilates the ureter, allows smooth evacuation of stones residues and avoids blockage within the ureter. It also allows healing of the mucosa after the procedure.
As the presence of this stent enables the urine to flow upwards into the kidney during urination, this may cause a painful sensation at first. The kidney generally becomes accustomed to it in a few days. After setting up the stent, it is recommended to drink abundantly5, to urinate regularly and not to force when urinate.
Regular side effects of your stent 6-8
- Pain, discomfort due to pressure that may increase when moving or after passing urine
- Encrustation of the stent: the formation of a thin coating of stone material on the stent
- Increased risk of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Bladder irritation symptoms include:
– Frequency
– Urgency
– Dysuria: painful or difficult urination
– Leakage
– Feeling of being unable to completely empty your bladder
- Hematuria: having blood in your urine
Don’t forget! You have a foreign body in you that will have to be removed in the weeks following its insertion.
Potential stent complications 7,8
- Migration or dislodgement of the stent
- Obstruction of the stent
- Rupture of the stent
- Erosion of the mucosa
How long will my stent stay in? 5,9
JJ Stent are intended to be placed in the body temporarily. During the treatment process of urinary stones, the JJ stents are left in place from a few days to few months, depending on the case, after which they must be removed. The JJ stent will be removed remotely, through the urinary tract, usually under local anaesthetic at a consultation (few minutes intervention) or sometimes under general anaesthetic.

|
Work:
If your job requires a significant amount of physical movement you may experience some pain and discomfort in your stomach and back area. |

|
Sex:
No specific contra-indications but some discomfort may occur during sexual activity. If your stent has a string, you may experience more discomfort and the stent may become dislodged. |
 |
Diet:
Nutritional guidelines could be proposed according to the nature of the stone. Your diet can remain the same, but ensure that you are drinking plenty of fluids (2 liters per day) after the procedure. If you are taking any medications, ask your doctor if it is okay to consume alcoholic beverages.
|
 |
Social Life:
Your social life should not be disrupted, but you may notice an increased frequency and urgency to use the restroom. |
 |
Exercise:
Activity may cause pain and discomfort in your stomach area. Avoid vigorous exercise. |
 |
Travel:
Before traveling, consult your doctor regarding your condition to see if it is safe. Your stent should not affect your ability to travel. |